
Take a look at your current data process environments. Chances are they run on a mixture of on-premises and cloud solutions, each of which is designed to kick-start a process with several downstream tasks, which in turn have corresponding pre- and post-dependencies. It’s a deluge of data for anyone to manage, and the days of using batch, cron, anacron, and other similar jobs with streaming data requirements have forced companies to rethink scheduling altogether.
In today’s modern data landscape, we should look at scheduling processes through an enterprise-wide lens:
Welcome to automating an enterprise’s modern data architecture! It can be overwhelming, even for a seasoned pro. But you don’t have to go it alone. It’s time to get to know your newest, most indispensable tool for in-cloud data orchestration: the enterprise scheduler.
An enterprise scheduler tool is designed to carry out repetitive tasks as defined in a schedule, which is based on calendar and event conditions. It enables enterprise systems and applications to interact together and orchestrate complex workflows across multiple servers and business applications. Enterprise schedulers also replicate time-consuming tasks without human intervention, run tasks outside working hours, and monitor jobs to notify users if errors occur.
The ideal enterprise scheduler will support date/time schedules, event triggers, and constraint-based scheduling, enabling IT to schedule and batch jobs across disparate applications and systems for end-to-end orchestration. For anyone looking to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows while easily applying semantics like retries, logging, dynamic mapping, caching, or failure notifications—this is your platform. Some enterprise schedulers even provide the ability to define workflows and tasks as code, making them more maintainable, versionable, testable, and collaborative.
Still contemplating whether enterprise schedulers are appropriate for your business? They can play a key role in streamlining operations maturity if you find yourself dealing with any of the following scenarios:
Now that you know when, let’s talk about which. To determine the right scheduler tool for your organization, start by picking a few popular scheduler tools and conduct your own comparative study of features, capabilities, and price. Some of the most popular scheduler tools include ActiveBatch, Control-M, Apache Airflow, and Prefect.
To make the most informed decision possible, some organizations opt to develop a Proof of Concept (PoC) of a few shortlisted scheduler tools to evaluate and compare features against licensing costs. Check out the table below for examples of enterprise scheduler features with associated activities that can be used for evaluation purposes.
| #
|
Scheduler features | Activities |
| 1 | Dependency & trigger management
|
Configure dependency criteria for workflows and tasks using the scheduler tool.
|
| 2 | Parallel execution
|
Create workflows with parallel tasks and update the relevant configuration files to allow parallel execution.
|
| 3 | Visualization of job setup and dependency views
|
View the workflows, associated tasks, last run, schedules, and other details in different scheduler visualization formats.
|
| 4 | Scheduling and triggering from UI
|
Schedule and trigger workflows from scheduler UI. Also, use the cron preset to define scheduled intervals.
|
| 5 | Execution status monitoring
|
Use scheduler workflow views to monitor execution status values including queued, running, success, failed, up_for_retry, up_for_reschedule, and skipped tasks.
|
| 6 | Start, pause, re-run, stop, resume, and prioritization features
|
Start workflows manually from UI (or) through schedules. Pause, stop, and re-run workflows through scheduler UI or CLI.
|
| 7 | Technology/platform agnostic
|
Create scheduler workflows encompassing jobs that span across multiple technology stacks used in your organization. |
| 8 | Notification, alerting, and integration with enterprise tools like job failures, long-running queries, etc.
|
Set email notifications either at workflow and/or task level for failure, long-running tasks (running above threshold), retries, etc.
|
| 9 | API access for job status and job details
|
Use scheduler APIs to return information for a task ID, the latest workflow runs, retrigger tasks, etc.
|
| 10
|
Code commit and deployment
|
Commit the scheduler workflow code in Git Repository or other code repositories and deploy through CI/CD process.
|
Ready to build a PoC of your own? Use the following evaluation approach—complete with steps and deliverables—to compare a few shortlisted enterprise scheduler tools.
Step 1: Determine the right use case for the scheduler PoC
Step 2: Setup enterprise schedulers
Step 3: Implement workflows orchestration on each enterprise scheduler tool
Step 4: Select the right enterprise scheduler tool by considering these factors
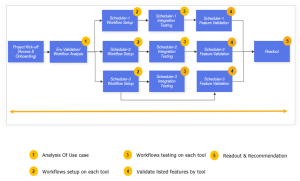
The diagram below shows the assessment flow while evaluating a PoC. As you can see, it involves multiple enterprise schedulers. Here, Scheduler-1, Scheduler-2, and Scheduler-3 refer to the enterprise scheduler tools that your organization is wanting to evaluate to make a decision.
Reading the terrain of the modern data landscape is no easy feat. But with the right enterprise scheduler tool at your command, you can turn a cacophony of in-cloud data into the sweetest symphony you (or your customers) have ever heard. It doesn’t matter how great your services are or how dedicated your team is if your organization is at the mercy of unruly data. Hopefully, after reading through our guide, you feel empowered to take the first step on your journey toward choosing the enterprise scheduling tool that works best for you.